Behind every successful AI agent is a strategically assembled team with the right mix of expertise and adaptability. While technology drives the capabilities of your agent, it’s the people behind it who shape its accuracy, ethics, and user experience.
AI agents are autonomous systems that perceive their environment, gather and process data, and execute complex tasks with minimal intervention. To bring this level of functionality to life, your team needs to cover a range of critical responsibilities, from data modeling and ML pipeline development to user experience and systems integration.
Thanks to the rise of no-code and low-code platforms like Relevance AI, building foundational agent capabilities is now more accessible than ever. However, whether you’re launching a proof of concept or scaling an enterprise-grade solution, having the right team in place remains a non-negotiable.
In the next two subsections, we’ll break down:
- The key roles every AI agent development team needs
- How to choose between building in-house talent or outsourcing to an external provider
Key Roles for AI Agent Development
 Building an AI agent is a coordinated effort that demands the right mix of skill sets, from leadership to data science. Assembling a focused, cross-functional team ensures your agent performs reliably, scales efficiently, and stays aligned with business goals.
Building an AI agent is a coordinated effort that demands the right mix of skill sets, from leadership to data science. Assembling a focused, cross-functional team ensures your agent performs reliably, scales efficiently, and stays aligned with business goals.
At the center is your Team Manager & Software Developer, who handles resource allocation, sets priorities, and keeps the development roadmap on track. Supporting them is a Documentation Manager, responsible for maintaining clear, version-controlled records of system changes and decision logs—a key asset for compliance and iteration.
You’ll also need a Data Scientist to interpret user behavior, identify workflow patterns, and recommend optimizations that inform both the model and business logic. Since AI agents learn and adapt over time, their performance depends on how well your team translates real-world data into actionable insights.
Additional roles—like a Quality Assurance Manager to monitor outputs, or a Product/AI Liaison to bridge tech and business objectives—ensure your agent doesn’t just function, but thrives in real-world applications.
If you're using platforms like OpenAI’s Agent SDK, many foundational tasks such as routing and basic agent logic are abstracted, letting your team focus on strategy, UX, and innovation rather than low-level engineering.
Here’s a quick overview:
| Role | Key Responsibility |
|---|
| Team Manager & Software Developer | Oversees execution, manages tasks and resources |
| Documentation Manager | Maintains accurate, up-to-date project records |
| Data Scientist | Extracts insights and predicts optimization paths |
With the right people in place, you're not just building an agent, you're creating an intelligent system that evolves with your business.
In-House vs. Outsourcing
 When it comes to building your AI agent, deciding between in-house development and outsourcing is more than a budget conversation, it’s a strategic call that can shape your long-term velocity, quality, and control.
When it comes to building your AI agent, deciding between in-house development and outsourcing is more than a budget conversation, it’s a strategic call that can shape your long-term velocity, quality, and control.
In-house development gives you full visibility and ownership of the project. You can tailor every component to your exact specs, align tightly with internal workflows, and retain complete control over your data and codebase. This approach is especially useful for projects requiring deep customization or tight integration with proprietary systems.
But that level of control comes at a cost. Recruiting experienced machine learning engineers, UX specialists, and data scientists can delay timelines and inflate overhead. Infrastructure costs—such as cloud usage, compute resources, and security—also scale quickly. And without clear direction, in-house teams can fall prey to technical drift.
Outsourcing, on the other hand, gives you access to specialized expertise and fast-tracked execution. You gain a plug-and-play development team that already knows how to ship—leveraging proven workflows, tools, and models. It’s particularly advantageous for startups and non-technical founders who need to move fast without sacrificing quality.
Still, outsourcing isn’t without risks. Without clear communication and strong alignment, quality assurance can falter. You may lose visibility into day-to-day progress unless the partner provides consistent checkpoints and collaborative transparency. That’s why selecting the right team matters just as much as choosing to outsource in the first place.
Here’s a quick comparison to help clarify your direction:
| Approach | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|
| In-House | Full control, deep customization, team proximity | High cost, longer timelines, recruiting challenges |
| Outsourced | Fast execution, access to top talent, lower overhead | Requires strong alignment and quality management practices |
It’s also worth noting: over 80% of AI models are never deployed—often due to performance issues or unclear scope. Avoiding that fate depends on choosing the right development approach and the right collaborators.
At AppMakers USA, we help companies evaluate both paths and offer hybrid solutions when needed. Whether you need full-service development or just expert augmentation, our agile workflows keep your project on track, delivering AI agents that actually launch, scale, and perform.
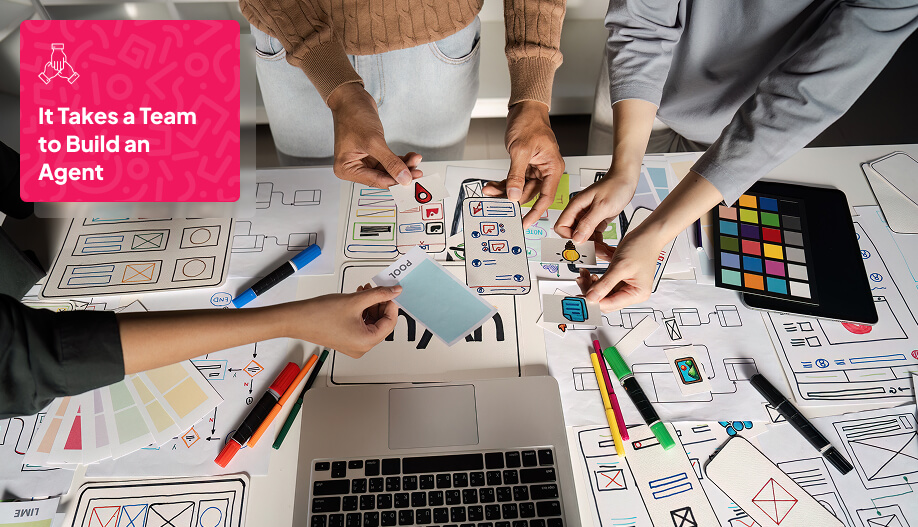











































 Building an AI agent
Building an AI agent




